Renewables to Dominate Electricity Generation Mix
“For the first time ever, in April 2019, renewable energy outpaced coal by providing 23 percent of US power generation, compared to coal’s 20 percent share.” With more people, governments, and companies realizing the benefits of renewable energy, this trend will likely continue. Clean, abundant energy can power almost anything with the right combination of technology and expertise.
In 2018, two-thirds of our electricity came from fossil fuels; by 2050, two-thirds of it will come from zero-carbon energy. The renewable energy industry is rapidly advancing and constantly introducing new, innovative ideas. As we learn more, we apply new designs to current systems and develop safer, more efficient, and more streamlined technology. Material costs are falling, and more governments and organizations are committing to greater use of alternative energy sources; these trends will drive the expansion of clean energy in the US and around the world.
New Energy Outlook 2019 found that more than two-thirds of the global population today live in countries where solar or wind, if not both, are the cheapest source of new electricity generation. PV module costs have decreased 89% since 2010 and they expect another 34% decline from today to 2030. Turbine costs are down 40% since 2010 and they expect the cost of wind energy to drop 36% by 2030. Additionally, battery storage is becoming more prevalent in solar and wind systems to offset the intermittent nature of these resources. Fortunately, lithium ion battery costs have declined by 35% in the first half of 2019 and enables these systems to be competitive with traditional generation sources.
Simultaneously, local interest in renewable energy has boomed and communities put pressure on city and state governments to step up their sustainability activities. 42 states and territories, including Washington D.C., have adopted either a renewable portfolio standard or have set renewable energy goals . They mandate that a certain percentage of electricity sold by utilities must come from renewable sources, thus helping diversify the states’ and territories’ energy resources, promote domestic energy production, and encourage economic development. This provides utilities an external push for clean energy improvements and holds individual governments accountable to their commitments.
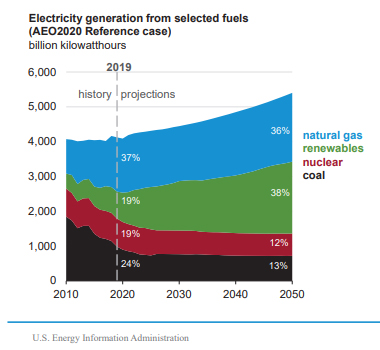
With these initiatives and decreasing costs of components, others will likely follow suit and invest in renewable energy systems as well. Companies and individuals will begin to purchase smaller systems for their immediate use and, over time, we can expect the United States’ electricity mix to become more diversified. Likewise, greater interest in renewables encourages investment into research for more efficient products. This in turn helps scale the industry and makes renewable energy more accessible to groups that didn’t consider it previously due to lack of knowledge or prohibitive costs and legislation. The joint efforts of governments, utilities, companies, and individuals will lead to substantial gains in the renewable energy sector. Hence, the US Energy Information Administration predicts 38% of electricity will be generated from renewables by 2050.
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Annual Energy Outlook 2020 (AEO2020) Reference case
We are already witnessing renewable energy’s potential to revolutionize the way in which the world generates electricity. Particularly with the advancement of battery storage technology, intermittent natural resources such as solar and wind are becoming significantly more competitive with traditional sources. It can make an electric grid more resilient and flexible, providing reliable power to users for generations to come. Moreover, renewable energy does not produce carbon dioxide emissions like coal or natural gas and can help mitigate the effects of climate change on a wide scale. We will undoubtedly continue to use electricity; why not get it from a cleaner source?